What Is a Pap Smear?
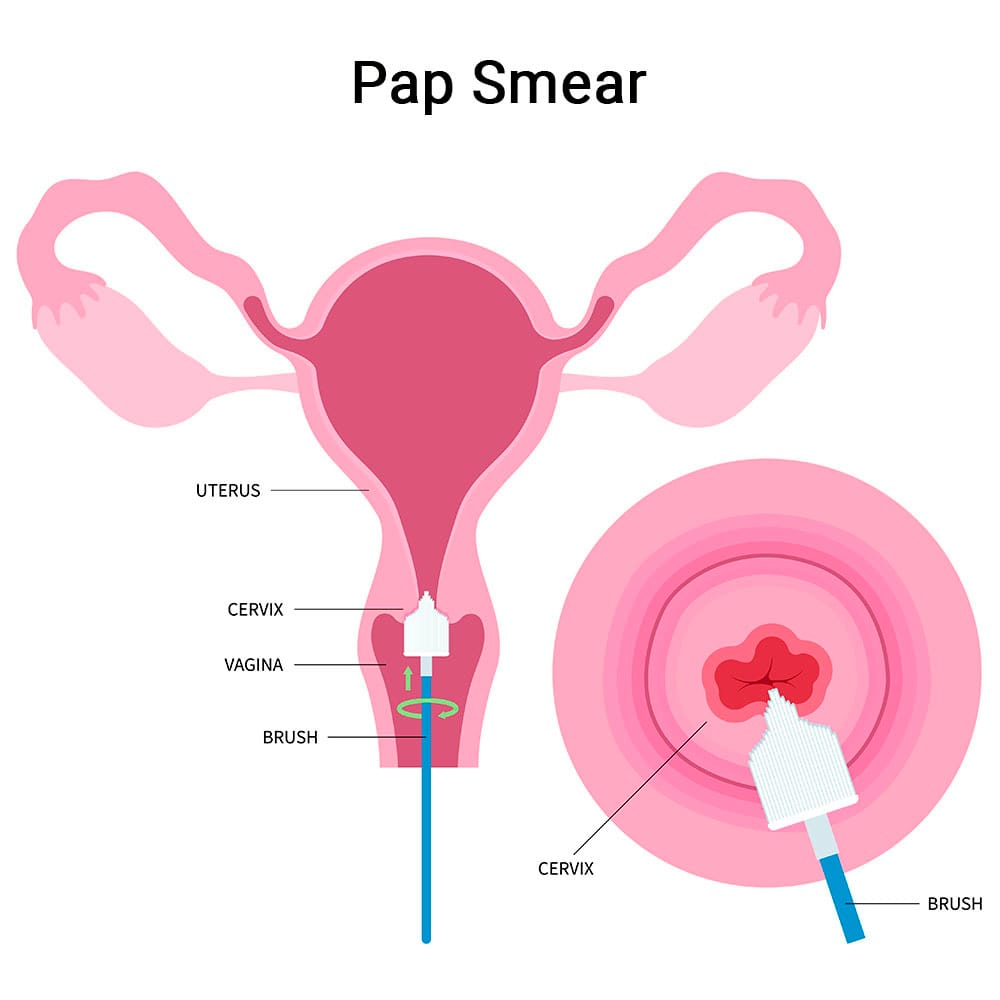 A Pap smear is a screening test that’s done to detect abnormal cells in your cervix that are cancerous or have the potential to become cancerous. During this test, cells are removed from your cervix so they can be closely examined under a microscope. It may be done along with an HPV test during a routine pelvic exam or your doctor may recommend this test if you have cervical cancer symptoms.
A Pap smear is a screening test that’s done to detect abnormal cells in your cervix that are cancerous or have the potential to become cancerous. During this test, cells are removed from your cervix so they can be closely examined under a microscope. It may be done along with an HPV test during a routine pelvic exam or your doctor may recommend this test if you have cervical cancer symptoms.
When you’re looking for top notch gynecological care in Midtown NYC, there’s no better choice than Cohen Medical Practice (CMP). If you’re looking for an annual gynecological exam, birth control or fertility services, visit CMP. If you’re concerned with symptoms such as pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding or urinary incontinence, Dr. Felix Cohen and his team of expert diagnosticians can find the answer.
When Do I Need a Pap Smear Test?
Screening for cervical cancer routinely is the best way to detect abnormal cells as early as possible. The earlier any abnormalities are detected, the better your chance of beating cervical cancer or any other condition.
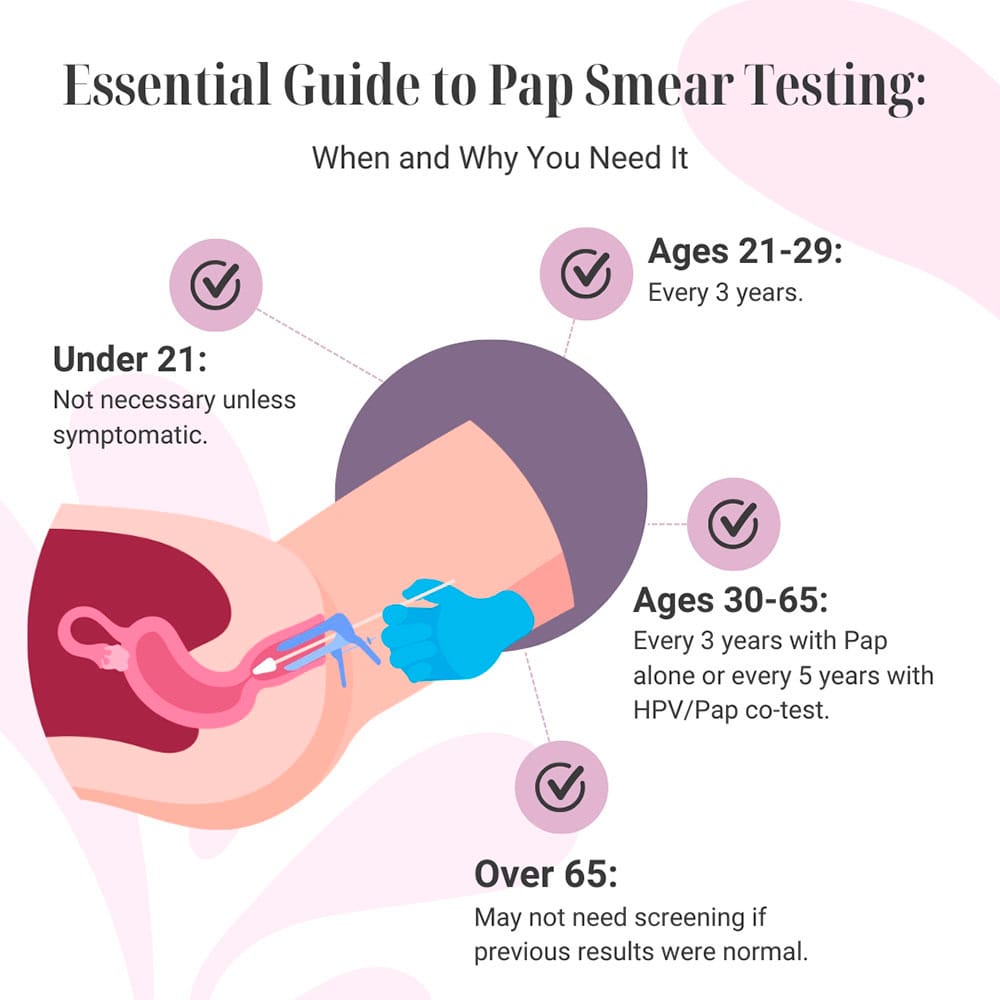
Recommendations for a routine Pap smear test varies based on age, such as:
- Under age 21. The risk of cervical cancer is low at this age, so Pap smears aren’t usually needed unless you have symptoms that concern you.
- In your 20s. Most women are advised to have their first Pap smear at age 21. If it’s normal, you can wait three years before having another one.
- Age 30 to 64. Pap tests should be done every three years. If you have a combination HPV/Pap test and both results are normal, you can wait five years before having another one.
- Over age 65. If you’ve been having regular Pap tests and results have been normal, your NYC gynecologist may tell you that you don’t need to be screened anymore.
Your doctor may recommend more frequent testing in certain situations such as having a history of cervical cancer, HIV or being immunocompromised. Even if it’s not time for your annual exam, schedule an appointment for a Pap smear test if you have cervical cancer symptoms.
These symptoms include:
- Menstrual periods that are heavier and longer than normal
- Vaginal discharge that’s watery, bloody or has a foul odor
- Vaginal bleeding between periods or after menopause
- Loss of appetite or unexplained weight loss
Pain during or after intercourse may be a sign of cervical cancer or may have another cause. It’s always best to talk to an expert in GYN conditions if sex is painful or if your periods are irregular or abnormal.
What Happens During a Pap Smear?
A Pap smear is done in your doctor’s office and only takes a few minutes. There’s no special preparation needed. To be sure your results are accurate, avoid douching, having sex or using spermicidal foams for two days before the test.
Steps of a Pap test include:
- Removing clothing from the waist down
- Lying on your back with your knees bent and your feet in stirrups
- Inserting a speculum into your vagina so the cervix can be seen clearly
- Taking sample cells from your cervix using a small soft brush
- Placing cells in a special liquid and sending them to a lab to be examined
When the speculum is inserted, you may feel some pressure, but a Pap smear isn’t usually painful. You may experience light bleeding after this test, but even that’s rare.
What Do My Pap Smear Results Mean?
It can take up to three weeks to receive your Pap smear results. If abnormalities are found, your gynecologist explains your treatment options or does further testing such as a repeat Pap smear or a colposcopy.
Results you may get from your Pap smear include:
- Negative, which means only healthy cervical cells were seen
- Unclear, which may mean you need follow-up testing
- Positive, which means abnormal cells were seen
When abnormal cells are identified from a Pap smear, it doesn’t always mean cancer.
Abnormal cells can fall into different categories, such as:
- Atypical squamous cells, which don’t look like cancer cells and may be a sign you need HPV treatment
- Squamous intraepithelial lesions, which are precancerous cells
- Atypical glandular cells that may or may not be cancerous and require further testing
- Squamous cell cancer or adenocarcinoma, which are most likely cancerous
If you’re diagnosed with an HPV infection, it can’t be cured, so HPV treatment focuses on removing genital warts and other warts caused by the virus. If you have an abnormal Pap smear during pregnancy, your doctor may order other tests, but if you need treatment, it’s likely to be delayed until after you have your baby.
Cohen Medical Practice (CMP) specializes in feminine health and aesthetic services, offering both surgical and nonsurgical treatment options. For expert, compassionate care for gynecological exams and services, abnormal Pap consultations, cancer screenings and more, contact Cohen Medical Practice (CMP) today.

