What Is a Urinary Tract Infection?
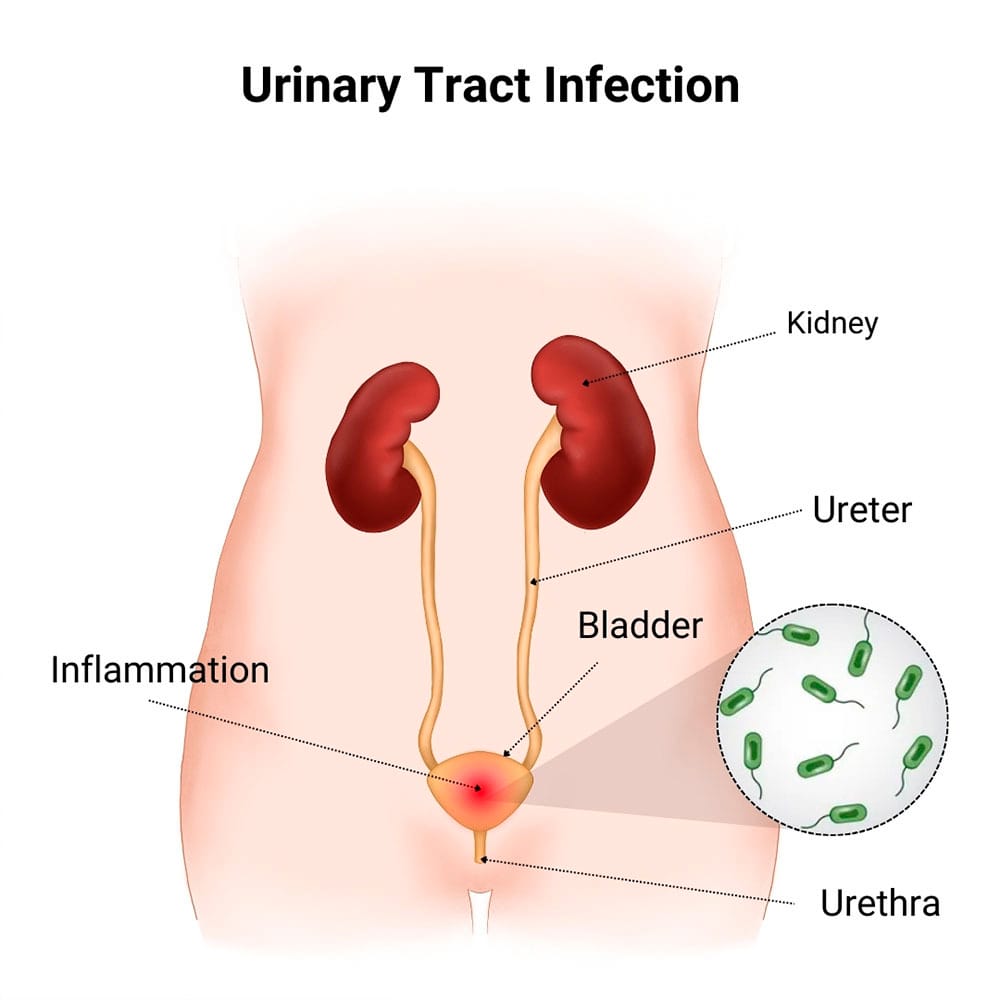 A urinary tract infection, commonly known as a UTI, is defined as a bacterial infection that affects different parts of the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters and urethra. Millions of people get UTIs each year and are treated successfully. However, untreated UTIs can lead to potential complications including sepsis, kidney damage and disease.
A urinary tract infection, commonly known as a UTI, is defined as a bacterial infection that affects different parts of the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters and urethra. Millions of people get UTIs each year and are treated successfully. However, untreated UTIs can lead to potential complications including sepsis, kidney damage and disease.
Since female UTIs can have staggering consequences if left untreated, at Cohen Medical Practice (CMP), you get the qualified medical help you need to receive the proper diagnosis and effective UTI treatment. This experienced team, led by Dr. Felix Cohen, has a deep understanding of how urinary tract infections affect the female reproductive system, and what are the common underlying causes. They have a comprehensive, personalized approach that ensures you get an effective solution.
What Are the Warning Signs of a UTI?
A UTI manifests in different ways in different people, so it’s important to recognize these signs to access early treatment. The gynecologists at CMP in Midtown NYC are familiar with these symptoms and can quickly differentiate a UTI and other conditions that may cause similar symptoms, such as various sexually transmitted diseases. Most people experience a burning sensation while urinating. You might also have the urge to urinate more frequently.
This urge may be persistent even when the bladder is empty. Other UTI symptoms include:
- Urine that’s cloudy and has a strong smell
- Bloody urine
- Pelvic pain
- Pain in the lower abdomen
How Do I Get Diagnosed for a UTI?
There are different diagnostic tests for UTIs, and your CMP gynecologist may use one or a combination for the most accurate diagnosis. Proper diagnosis is also helpful in determining any underlying conditions to offer a comprehensive treatment plan and prevent recurrence.
The gynecologist starts with a review of your medical history. They may ask some questions on issues such as hygiene and sexual habits. They also do a physical examination.
Other diagnostic procedures include:
- Urinalysis. A urine sample is collected for examination of the chemical and physical characteristics of the urine.
- Culture test. A sample of your urine is tested to check for bacterial growth.
- Imaging tests. This may include an ultrasound, CT scan or MRI test to visualize your urinary tract for identification of any abnormalities.
Why Do I Keep Getting UTIs?
A UTI is primarily a bacterial infection caused by common bacteria such as e. coli and klebsiella. In most cases, these bacteria find their way into the urinary tract when they’re pushed from the rectum into the urinary tract.
It’s not uncommon for a UTI to recur after treatment. This usually happens when you don’t complete the treatment, leaving bacteria in the urinary tract.
Recurrence also happens when the underlying risk factors are not addressed, including:
- Anatomical abnormalities. Urinary tract abnormalities such as a small bladder or a urethra that’s too narrow encourage bacterial growth.
- Weakened immunity. Poor health occasioned by ailments such as cancer or HIV, which leave the body exposed to repeated bacterial infections.
- Poor hygiene. Lack of proper hygiene such as not wiping or wiping improperly after using the bathroom provides a rich environment for bacterial growth and spread.
How Do I Get Treated for a UTI?
The treatment for a UTI varies depending on the section of the urinary tract affected and the severity of the infection. Some severe cases require hospitalization for intravenous administration of medication and proper follow-up.
But in the majority of cases, a UTI is treated in the outpatient clinic or your doctor’s office, and you go home the same day.
Your gynecologist may use one or a combination of the following treatment options:
- Antibiotics. The gynecologist can prescribe the most effective antibiotic against the bacteria identified. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin and nitrofurantoin.
- Pain relief medication. You receive a short supply of drugs to help with the burning sensation and other pain.
- Behavioral changes. Your NYC gynecologist also discusses habitual changes you need to make, such as developing better hydration and proper hygiene practices.
When Is Surgery Necessary for Treating a UTI?
Surgery is usually the last option for treating a UTI but may be necessary in some cases. This is more so when UTIs recur because of anatomical abnormalities. Surgery is also used to clear an obstruction or blockage in the urinary tract.
Your CMP gynecologist works with you to determine if surgery is the best option after considering your fitness for this option.
Some of the minimally invasive surgical techniques used for UTI treatment include:
- Cystoscopy. This procedure uses a scope to examine the urethra and bladder when the cause isn’t immediately evident.
- Ureteroscopy. This is a surgical procedure used to clear urinary tract blockages.
- Nephrostomy. During this procedure, the surgeon makes an opening in the kidneys to drain fluids.
While UTIs may not be life-threatening, they cause significant disruptions and discomfort. The discomfort and frequent urges to urinate disrupt life significantly. Seek treatment as early as possible to avoid more serious complications, including kidney disease and the spread of infection to other parts of your body.
After menopause, symptoms may be more serious and include:
- Increased heart rate
- Urinary incontinence
- Decreased appetite
- Delirium
- Fatigue
- Loss of balance
- Low blood pressure
The team at Cohen Medical Practice (CMP) has resources to offer comprehensive treatment for UTIs and other gynecological problems. Contact Cohen Medical Practice (CMP) today to schedule an appointment to get a personalized treatment plan that works for you.

