What Are Genital Warts?
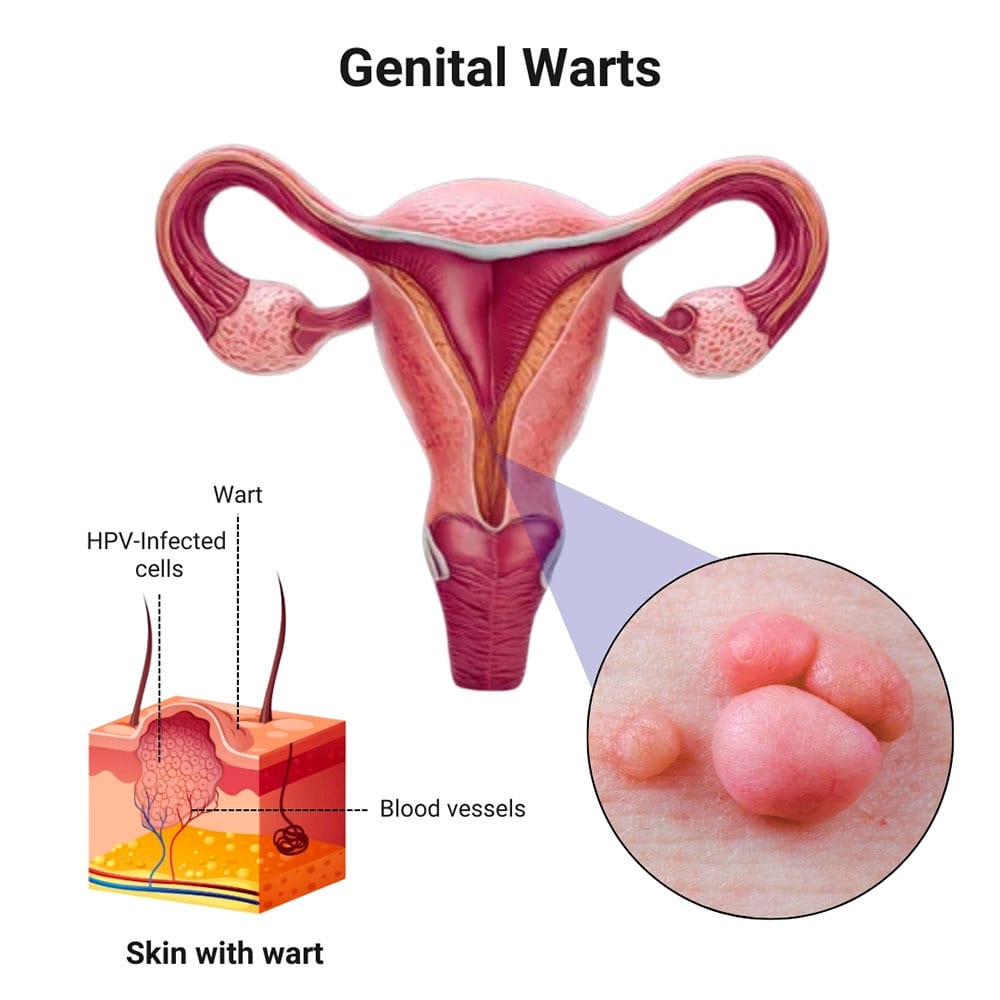 Small skin-colored bumps or groups of bumps that form around your genitals and rectum may be genital warts, a type of sexually transmitted disease (STD). Genital warts are a common infection caused by certain strains of the human papilloma virus (HPV). These warts are sometimes tiny and difficult to see. It’s vital that you seek medical attention at the first sign of the bumps to prevent the spread of the condition and avoid more serious consequences that could even include infertility.
Small skin-colored bumps or groups of bumps that form around your genitals and rectum may be genital warts, a type of sexually transmitted disease (STD). Genital warts are a common infection caused by certain strains of the human papilloma virus (HPV). These warts are sometimes tiny and difficult to see. It’s vital that you seek medical attention at the first sign of the bumps to prevent the spread of the condition and avoid more serious consequences that could even include infertility.
If you suspect you may have HPV warts or any other type of STD, make an appointment at a reputable Midtown NYC gynecology practice. The best choice is Dr. Felix Cohen, a best Midtown, NYC gynecologists. He’s also the founder and director of Cohen Medical Practice (CMP).
How Is HPV Transmitted?
There are many types of the HPV virus and not all of them cause genital warts. STDs are spread through sexual contact, so you can get genital warts from oral, vaginal or anal sex. HPV can also be spread if there’s skin to skin contact without ejaculation.
There are certain things that increase your risk of becoming infected with HPV, such as:
- Having sex with more than one partner
- Not using a condom
- Becoming sexually active at a young age
- Having a weakened immune system
- Not having the HPV vaccine
Your risk of infection increases if you don’t know the sexual history of a sexual partner. If you’ve previously had another STD, such as chlamydia, syphilis, HIV or gonorrhea, it can also increase the risk of becoming infected with HPV. Using a condom reduces the chances of becoming infected, but it doesn’t completely eliminate the risk of contracting the virus or spreading it to others.
Do Genital Warts Hurt?
Genital warts don’t usually hurt, and mild genital warts may not cause any noticeable symptoms. These HPV bumps may appear on the vulva, vagina, penis, mouth or throat. Characteristics of the appearance of genital warts include:
- Small or large lumps or bumps
- Bumps that are raised or flat
- Groups of warts that are shaped like a cauliflower
Genital warts can disappear on their own, or they can grow in size and number, making it all the more important to get tested.
Other symptoms you may experience include:
- Itching or irritation in your genital area
- Burning sensation
- Mild vaginal bleeding during or after sex
- Increased vaginal discharge
Genital warts may appear within a few weeks after sexual contact with an infected person. Sometimes symptoms don’t appear for months or even years.
How Do I Know if I Have Herpes or Genital Warts?
Genital herpes is another condition that’s caused by a virus that’s sexually transmitted.
When comparing genital warts vs. herpes, ways that herpes differs include:
- Herpes usually leads to fluid filled blisters, while HPV bumps are small and don’t usually cause open sores.
- With herpes, lesions can be painful.
- Herpes may be accompanied by flu-like symptoms.
- Genital herpes may cause urination to be difficult or painful.
Your NYC gynecologist can usually diagnose genital warts by looking at them during a pelvic exam. Your doctor may also do a Pap smear or take a tissue sample to send to the lab. To see warts that aren’t visible to the naked eye, an exam called a colposcopy may be done. Both herpes and genital warts are contagious and infections can be passed on even if there are no symptoms.
Is HPV Curable?
Treatment of HPV is available, but there’s no cure. Genital warts may eventually go away on their own, but if they do, you still carry the virus and can pass it on. You can, however, treat genital warts if they’re uncomfortable or itchy.
Treatment options include:
- Prescribed medication. Your doctor can prescribe topical lotions or ointments that boost your immune system or destroy genital warts. Don’t use over-the-counter wart removal medication for genital warts.
- Electrocautery. In this procedure, an electric current is used to burn off warts.
- Cryotherapy. This is done by using liquid nitrogen to freeze the warts. This forms a blister around the wart, and it eventually falls off. Several treatments may be required.
- Laser treatments. This option is done using an intensive beam of light and may be used for genital warts that resist other approaches to treatment.
- Surgical excision. Genital warts can be removed during a surgical procedure.
After one of these procedures, you may experience irritation or soreness for a few days. In some people, the warts return. Some types of HPV are preventable with a vaccine that can be given up to age 45. Using a condom the right way and being in a mutually monogamous relationship also reduces the risk of contracting HPV or other STDs.
If you have lumps, bumps or sores in your genital area, you need a knowledgeable and experienced specialist in feminine health for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. That’s exactly what you’ll find when you see Dr. Felix Cohen at CMP New York. For a routine annual exam or for treatment of STDs or other gynecological conditions, contact CMP New York today.

