What Are Ovarian Polyps and How Do They Differ from Other Growths?
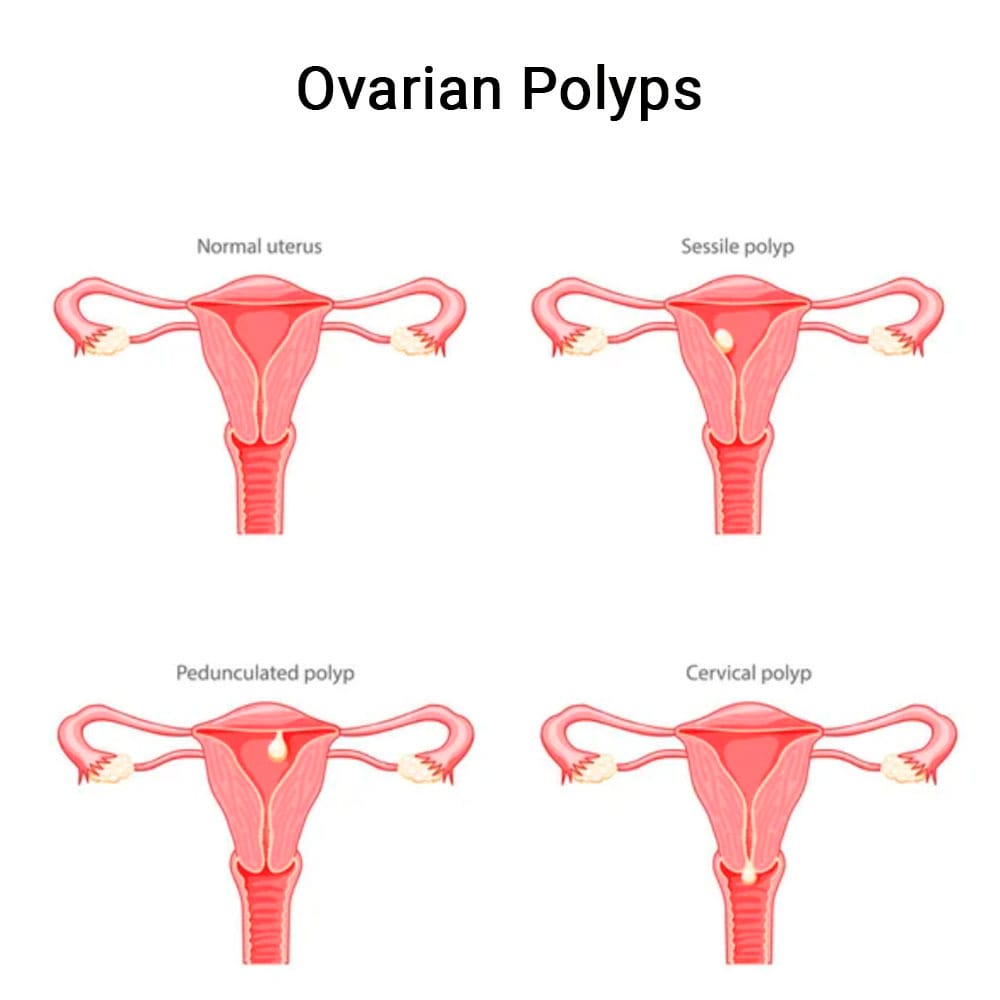 Ovarian polyps are benign ovarian tumors primarily caused by abnormal growth of cells. These growths are often mistaken for diseases like ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids. However, polyps are solid tissue masses and usually require intervention, whereas cysts result from hormone imbalance and may resolve spontaneously.
Ovarian polyps are benign ovarian tumors primarily caused by abnormal growth of cells. These growths are often mistaken for diseases like ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids. However, polyps are solid tissue masses and usually require intervention, whereas cysts result from hormone imbalance and may resolve spontaneously.
Some key differences include:
- Ovarian polyps vs. endometrial polyps. Both typically are benign; however, they form in different locations of the body — the ovaries versus the lining inside the uterus.
- Cervical polyps. These are formed on the cervix, as polyps can be found almost anywhere.
- Ovarian polyps vs. cysts. Cysts are benign, fluid-filled sacs. Polyps, on the other hand, involve tissue-based growths that are less likely to resolve without intervention.
In some cases, ovarian polyps can be linked to other disorders like endometriosis, which causes uterine lining cells to grow outside the uterus, and pelvic inflammatory disease, which can cause inflammation in the entire reproductive system. To ensure that you receive an accurate diagnosis, since symptoms are so similar to other conditions, you need an expert in female health like you find at Cohen Medical Practice (CMP) in Midtown NYC. Dr. Felix Cohen and his expert colleagues provide exceptional diagnostic practices, which lead to the most effective treatments.
What Are the Symptoms of Ovarian Polyps?
Ovarian polyps may not always cause symptoms, especially when the polyps are small. Larger ovarian polyps can cause a variety of concerns, usually mimicking other conditions with symptoms such as abnormal uterine bleeding and pelvic pain.
Common symptoms of ovarian polyps include:
- Pain in the pelvic area during menstruation or intercourse
- Irregular bleeding or bleeding between periods
- Feeling bloated or over full
- Incontinence or the need to urinate more often due to pressure in the bladder
- Unexplained weight gain and fluctuation of weight
- Lower back pain with aches in the thighs as well
- Nausea or vomiting due to large cyst size or rupture
- Painful passing of stools due to pressure on the rectum
If you address such issues at an early stage with the help of Dr. Cohen, you can avoid complications and obtain the best possible treatment for your reproductive health.
What Causes Ovarian Polyps and How Are They Diagnosed?
Ovarian cysts or cervical polyps most often result from hormonal imbalance, with a surfeit of estrogen most of the time. Among the factors that contribute to this problem are endometriosis and adenomyosis, where endometrial tissue has grown outside the uterus.
Other conditions may also increase the complexity of ovarian polyps, such as:
- Hormonal changes accompanied by increases in estrogen
- Genetic predisposition or family background
- Co-existing conditions of endometrial polyps or uterine fibroids
Medical history, physical examination and imaging studies are used in diagnosing ovarian polyps. Transvaginal ultrasound is a commonly used visual imaging technique for detecting polyp sizes and locations.
Abnormal conditions can be detected through additional tests, including:
- Pelvic exam. Your doctor physically examines the ovaries to check for any disorders.
- Hysteroscopy. The examination with a camera is used to visually inspect the uterus and the ovaries.
- Endometrial biopsy. A procedure that may be performed when your CMP New York doctor suspects endometrial polyps or other diseases.
Precise diagnosis will rule out other diseases like ovarian cysts or ovarian tumors that would have different treatment protocols.
What Are the Treatment Options for Ovarian Polyps?
The source of your symptoms must first be understood to administer appropriate therapy. The treatment of ovarian polyps depends on the size of the growths, severity of your symptoms and your general health.
If the polyps are small and asymptomatic, your CMP gynecologist may recommend waiting for them to resolve. More urgent action may, however, be required when the polyps are symptomatic.
Treatment options may include:
- Medications. Hormonal replacement therapy or different types of birth control pills, regulate hormones and prevent the establishment of new polyps.
- Surgical removal. If the polyps are more significant or symptomatic, surgery through minimally invasive laparoscopy is conducted to remove the mass.
- Hysteroscopic myomectomy or polypectomy. In cases where endometrial and ovarian polyps co-exist, this procedure is conducted to remove both growths simultaneously.
These treatments are very effective, and recovery can be swift, primarily when handled by skilled specialists who use modern gynecological techniques, producing shorter procedure times, less pain and lower risk for complications.
What’s the Recovery Process after Ovarian Polyp Extraction?
Recovery after ovarian polyp extraction is usually unproblematic in general. Especially when minimally invasive procedures, such as laparoscopic surgery, are employed. Most women return to their normal activities shortly after the procedure. The recovery process usually includes pain relief handled with over-the-counter pain relievers and minimal side effects like mild cramping or spotting.
By following the post-surgical instructions from your doctor closely, you avoid the re-emergence of polyps or development of other significant complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease. Contact Cohen Medical Practice (CMP) in Midtown NYC for top-tier gynecological care with personalized treatments, ensuring your health is prioritized with expert care.

