What Is Pregnancy Genetic Testing?
Prenatal genetic testing provides information about your baby’s genetic makeup, particularly about the risk of inherited conditions or birth defects before birth. Even if you’re not at high risk, every pregnancy carries a small chance of birth defects or genetic disorders. Unlike routine prenatal tests, such as checking blood type, glucose levels or hemoglobin count, a prenatal genetic test is optional. It provides deeper insights into your baby’s development.
Making decisions regarding your pregnancy or future fertility may feel overwhelming, so gather the right information, which makes all the difference. Cohen Medical Practice (CMP New York) in Manhattan offers a comprehensive range of genetic testing services to help you take charge of your baby’s health with confidence and clarity. This medical practice, led by Dr. Felix Cohen, also provides access to professional genetic counseling and family history risk assessment services. Under the leadership of, a board certified OB-GYN and founder of the Midtown NYC practice.
What Are the Different Types of Prenatal Genetic Tests?
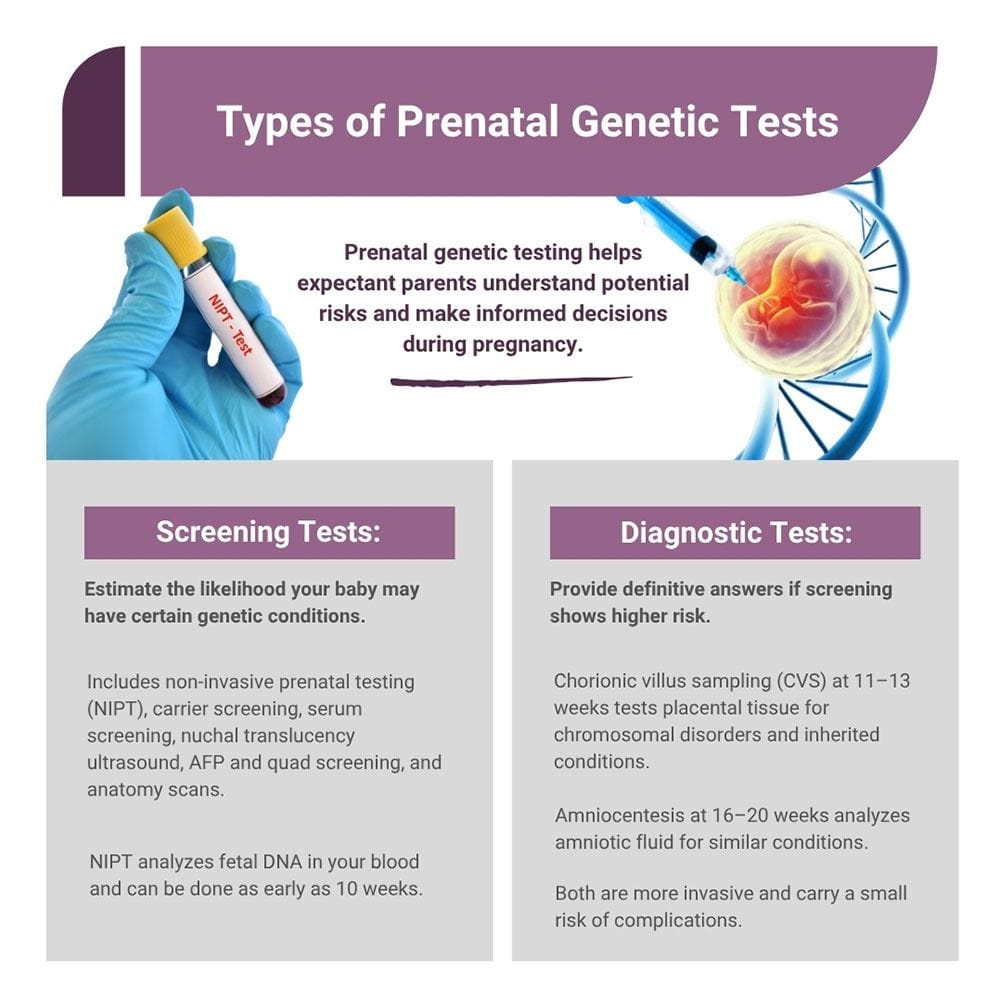
There are two main categories of prenatal genetic testing include screening tests and diagnostic tests. Prenatal genetic screening tests estimate the chance that your baby may have certain genetic conditions. These screening tests, such as common non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), carry no risk to your baby. It’s a blood test that analyzes the small pieces of fetal DNA that are present in your bloodstream.
You can have a panorama test, a type of NIPT, as early as 10 weeks into your pregnancy. Early detection at nine weeks is available if you’re worried about the viability of the fetus.
Other prenatal genetic screening tests include:
- Carrier screening
- Serum screening
- Nuchal translucency
- AFP screening
- Quad screening
- Anatomy scanning
Diagnostic tests may be warranted if your genetic screening test shows a higher risk for a specific genetic condition. Your doctor may recommend a chorionic villus sampling (CVS) between 11 to 13 weeks or an amniocentesis between 16 to 20 weeks. Both tests check for chromosomal disorders, neural tube defects and inherited conditions. CVS uses a small sample of placental tissue to provide earlier results, while amniocentesis analyzes the amniotic fluid later in your pregnancy. These diagnostic tests give you clearer answers, but are more invasive. There’s also a small risk of complications, including miscarriage.
Am I a Good Candidate for Pregnancy Genetic Testing?
You may be a candidate for pregnancy genetic testing if you’re 35 or older by the time of your scheduled delivery. The risk of chromosomal abnormalities in your child rises as you get older. Testing can help you understand the likelihood of such conditions early on in pregnancy. Your Manhattan obstetrician may recommend tests if you or your partner have a personal or family history of genetic disorders, such as:
- Cystic fibrosis
- Sickle cell disease
- Tay-Sachs disease
- Thalassemia
Previous pregnancies with an abnormal outcome also make you a good candidate for genetic testing. If you’ve experienced multiple miscarriages or a stillbirth, testing may offer insights into whether a genetic issue played a role. If any of these factors apply to you, consider a preconception genetic test before you get pregnant.
What Do the Genetic Test Results Mean for My Pregnancy?
Your genetic test results typically show whether your baby is at increased or decreased risk for certain genetic or chromosomal conditions. For screening tests like an NIPT or a serum screening, your results aren’t definitive. Instead, they indicate the likelihood of a condition being present.
If you receive high-risk results from a screening test, your doctor may discuss your next steps, such as a:
- Meeting with a genetic counselor
- Thorough review of your personal and family medical history
- Decision about proceeding with diagnostic testing
It’s possible your genetic test results are inconclusive or even inaccurate. False positives occur where a test suggests high risk, but the baby is healthy. False negatives are less common, but possible. In some cases, your test may fail to provide any result due to low levels of fetal DNA in your blood. False positives can be proven through diagnostic testing.
How Does CMP New York Ensure My Safety During Genetic Testing?
At CMP New York, your safety and comfort are top priorities during every stage of genetic testing. These medical professionals emphasize non-invasive prenatal testing methods whenever possible. Tests like NIPT are conducted through simple blood draws that pose no harm to you or your baby.
A key advantage of CMP new York’s genetic testing is early detection at nine weeks of pregnancy. When advanced diagnostic procedures are recommended, a skilled doctor like Dr. Cohen, a board certified OB-GYN, performs them with precision and care.
This Midtown Manhattan practice creates a calming atmosphere with a welcoming staff, modern amenities and a focus on a patient-centered approach. The team includes trained clinicians who take the time to explain procedures, answer questions and reassure you throughout the testing process. To get started with personalized care, book an appointment today for pregnancy genetic testing services.
They also offer:

